 |
Manith's Website Tutorial |
 |
I learned HTML from the website W3schools |
Pls review me website from down bellow |
Website's Reviews Website's ChangeLog Website Online Link View Website Code W3 Profile
Content Library
Lesson 1 - HTML Introduction
What is HTML?
HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages.
- HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
- HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages
- HTML describes the structure of a Web page
- HTML consists of a series of elements
- HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content
- HTML elements label pieces of content such as "this is a heading",
"this is a paragraph", "this is a link", etc.
Example of HTML Code
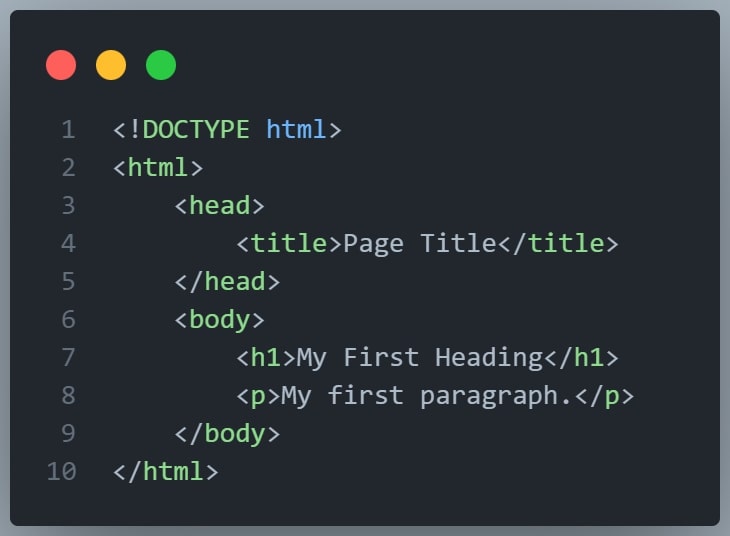
- The
<!DOCTYPE html>declaration defines that this document is an HTML5 document - The
<html>element is the root element of an HTML page - The
<head>element contains meta information about the HTML page - The
<title>element specifies a title for the HTML page (which is shown in the browser's title bar or in the page's tab) - The
<body>element defines the document's body, and is a container for all the visible contents, such as headings, paragraphs, images, hyperlinks, tables, lists, etc. - The
<h1>element defines a large heading - The
<p>element defines a paragraph
This is what h1 to h6 looks like
This is H1
This is H2
This is H3
This is H4
This is H5
This is H6
What is an HTML Element?
An HTML element is defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag:
The HTML element is everything from the start tag to the end tag:
Ex:- <tagname> Content goes here... </tagname>
<h1> My First Heading </h1>
<p> My First Paragraph. </p>

Note: Some HTML elements have no content (like the <br> element). These elements are called empty elements. Empty elements do not have an end tag!
Web Browsers
The purpose of a web browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari) is to read HTML documents and display them correctly.
A browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses them to determine how to display the document:
HTML Page Structure (Very Important For Beginners)
Below is a visualization of an HTML page structure:
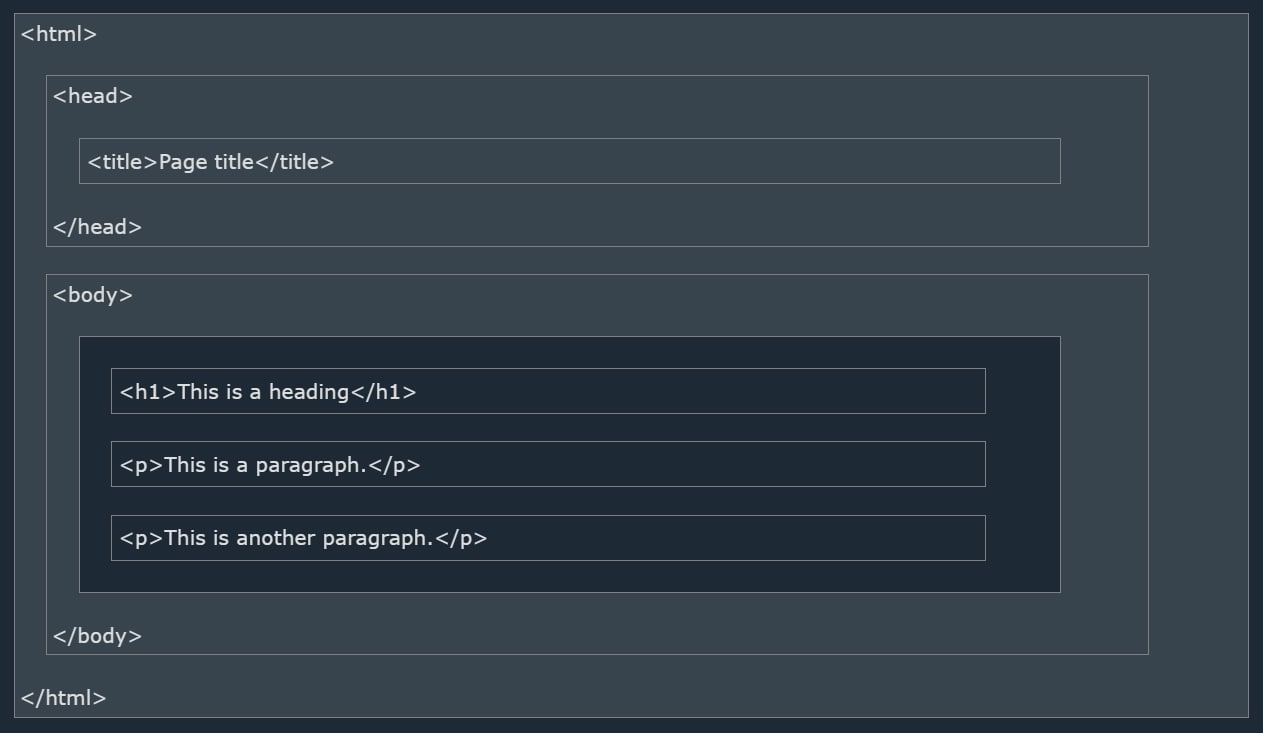
Note: The content inside the <body> section will be displayed in a browser.
The content inside the <title> element will be shown in the browser's title bar or in the page's tab.
HTML History (Not very Important)
| Year | Version |
|---|---|
| 1989 | Tim Berners-Lee invented World Wide Web (www) |
| 1991 | Tim Berners-Lee invented HTML |
| 1993 | Dave Raggett drafted HTML+ |
| 1995 | HTML Working Group defined HTML 2.0 |
| 1997 | W3C Recommendation: HTML 3.2 |
| 1999 | W3C Recommendation: HTML 4.01 |
| 2000 | W3C Recommendation: XHTML 1.0 |
| 2008 | WHATWG HTML5 First Public Draft |
| 2012 | WHATWG HTML5 Living Standard |
| 2014 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5 |
| 2016 | W3C Candidate Recommendation: HTML 5.1 |
| 2017 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5.1 2nd Edition |
| 2017 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5.2 |
This Website created By Manith Fernando teaches HTML5.2
Lesson 2 - HTML Elements
HTML Elements
The HTML element is everything from the start tag to the end tag:
<tagname> Content goes here... </tagname>
Examples of some HTML elements:
<h1> My First Heading </h1>
<p> My first paragraph </p>
Nested HTML Elements
HTML elements can be nested (this means that elements can contain other elements).
All HTML documents consist of nested HTML elements.
The following example contains four HTML elements (<html>,<body>,<h1> and <p>):
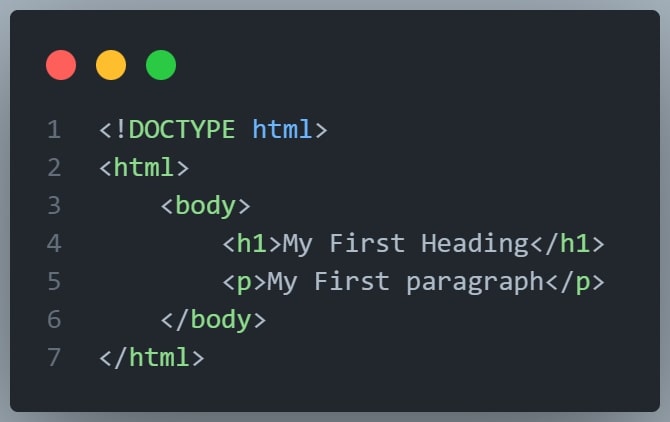
Example Explained
The <html> element is the root element and it defines the whole HTML document.
It has a start tag <html> and an end tag </html>
Then, inside the <html> element there is a <body> element:.
The <body> element defines the document's body.
It has a start tag <body> and an end tag </body>
Then, inside the element there are two other elements: <h1> and <p>
The <h1> element defines a heading.
It has a start tag <h1> and an end tag </h1>
The <p> element defines a paragraph.
It has a start tag <p> and an end tag </p>
Never Skip the End Tag
Some HTML elements will display correctly, even if you forget the end tag:
Empty HTML Elements
HTML elements with no content are called empty elements.
The <br> tag defines a line break, and is an empty element without a closing tag:
HTML is Not Case Sensitive
HTML tags are not case sensitive: <P> means the same as <p>.
HTML Tag Reference
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
<html> |
Defines the root of an HTML document |
<body> |
Defines the document's body |
<h1> to <h6> |
Defines HTML headings |
For a complete list of all available HTML tags, visit this website called HTML Tag Reference since it may take me 128 hours to make it all if I made a table by myself.
Lesson 3 - HTML Attributes
HTML Attributes
- All HTML elements can have attributes
- Attributes provide additional information about elements
- Attributes are always specified in the start tag
- Attributes usually come in name/value pairs like: name="value"
The href Attribute
The <a> tag defines a hyperlink. The href attribute specifies the URL of the page the link goes to:
Example
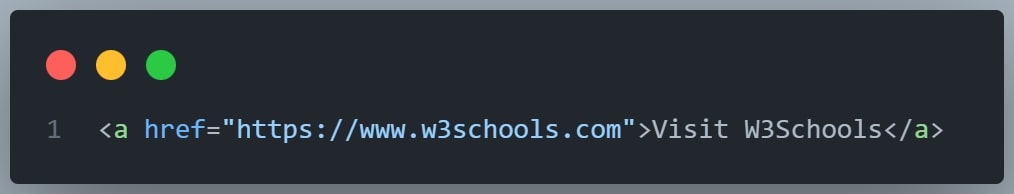
You will learn more about links on a later lesson
The src Attribute
The <img> tag is used to embed an image in an HTML page.
The src attribute specifies the path to the image to be displayed:
Example
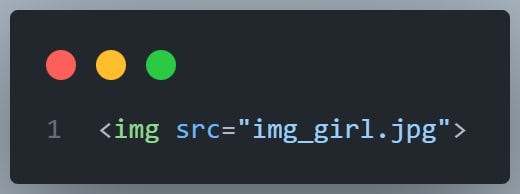
There are two ways to specify the URL in the src attribute:
1. Absolute URL
Links to an external image that is hosted on another website. Example: src="https://www.w3schools.com/images/img_girl.jpg".
Notes: External images might be under copyright. If you do not get permission to use it, you may be in violation of copyright laws. In addition, you cannot control external images; it can suddenly be removed or changed.
2. Relative URL
Links to an image that is hosted within the website. Here, the URL does not include the domain name. If the URL begins without a slash, it will be relative to the current page. Example: src="img_girl.jpg". If the URL begins with a slash, it will be relative to the domain. Example: src="/images/img_girl.jpg".
Tip: It is almost always best to use relative URLs. They will not break if you change domain.
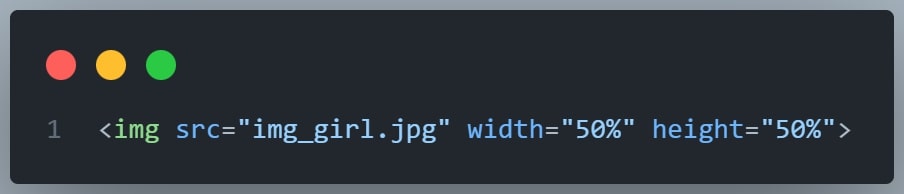
The width and height Attributes
The <img> tag should also contain the width and height attributes, which specify the width and height of the image
In pixels:
In percentages
The alt Attribute
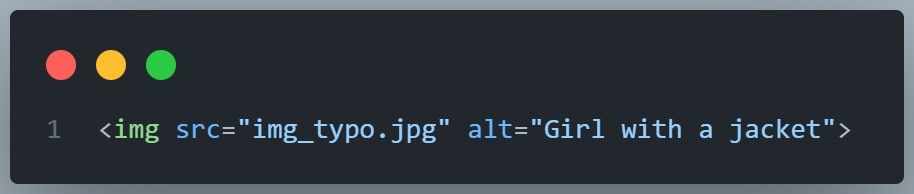
The required alt attribute for the <img> tag specifies an alternate text for an image, if the image for some reason cannot be displayed.
This can be due to a slow connection, or an error in the src attribute, or if the user uses a screen reader.
Example
See what happens if we try to display an image that does not exist:
You will learn more about images in this HTML Images chapter.
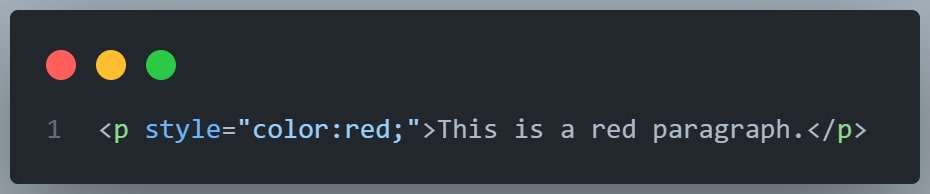
The style Attribute
The style attribute is used to add styles to an element, such as color, font, size, and more.
Example
You will learn more about styles in this HTML Styles chapter
The lang Attribute
You should always include the lang attribute inside the <html> tag, to declare the language of the Web page. This is meant to assist search engines and browsers.
The following example specifies English as the language:

Country codes can also be added to the language code in the lang attribute.
So, the first two characters define the language of the HTML page, and the last two characters define the country.
The following example specifies English as the language and Australia as the country:

You can see all the language codes in this HTML Language Code Reference.
For a complete list of all attributes for each HTML element visit this HTML Attribute Reference Website.
Lesson 4 - HTML Styles,CSS
CSS stands for "Cascading Style Sheets".
CSS saves a lot of work. It can control the layout of multiple web pages all at once.
What is CSS?
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is used to format the layout of a webpage.
With CSS, you can control the color, font, the size of text, the spacing between elements, how elements are
positioned and laid out, what background images or background colors are to be used, different displays for
different devices and screen sizes, and much more!
Using CSS
CSS can be added to HTML documents in 3 ways:
- Inline - by using the
styleattribute inside HTML elements - Internal - by using a
<style>element in the<head>section - External - by using a
<link>element to link to an external CSS file
The most common way to add CSS, is to keep the styles in external CSS files.
Inline CSS
An inline CSS is used to apply a unique style to a single HTML element.
An inline CSS uses the style attribute of an HTML element.
The following example sets the text color of the <h1> element to blue, and the text color of the <p> element to red:
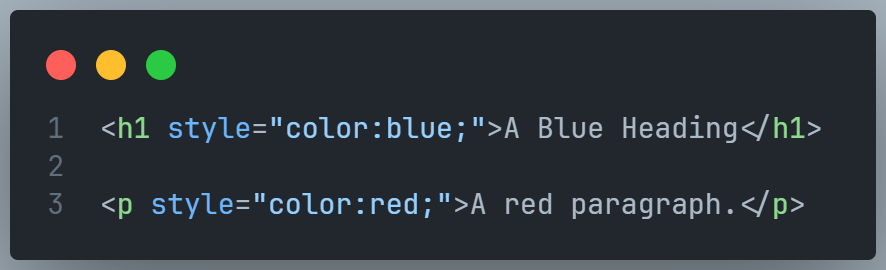
Internal CSS
An internal CSS is used to define a style for a single HTML page.
An internal CSS is defined in the <head> section of an HTML page, within a <style> element.
The following example sets the text color of ALL the <h1> elements (on that page) to blue, and the text color of ALL the <p> elements to red. In addition, the page will be displayed with a "powderblue" background color:
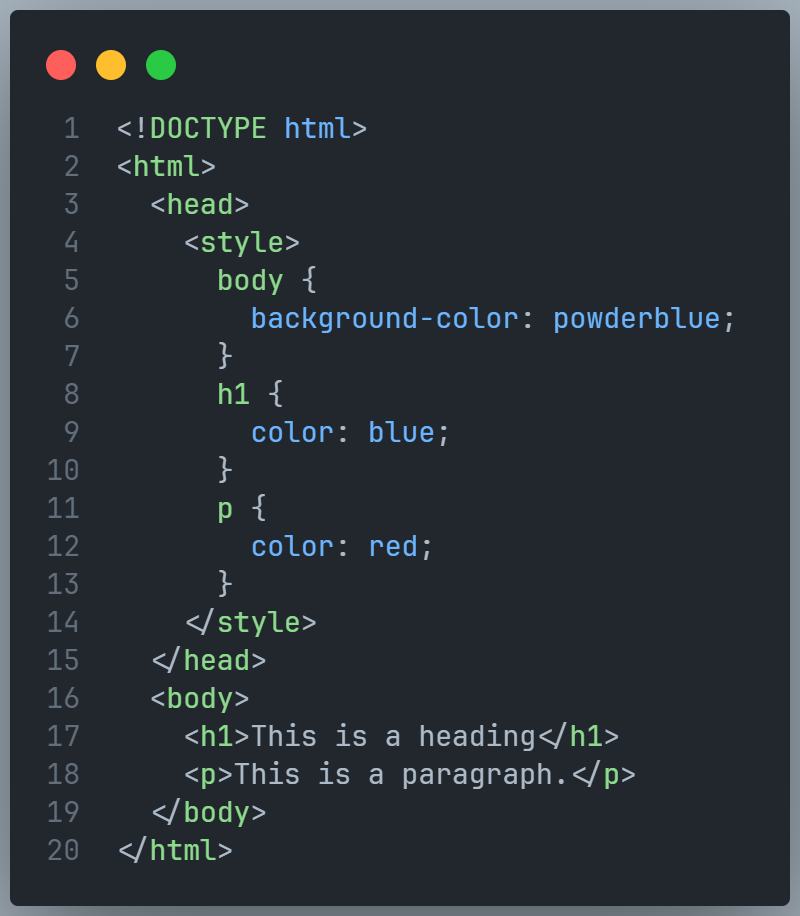
External CSS
An external style sheet is used to define the style for many HTML pages.
To use an external style sheet, add a link to it in the <head> section of each HTML page:
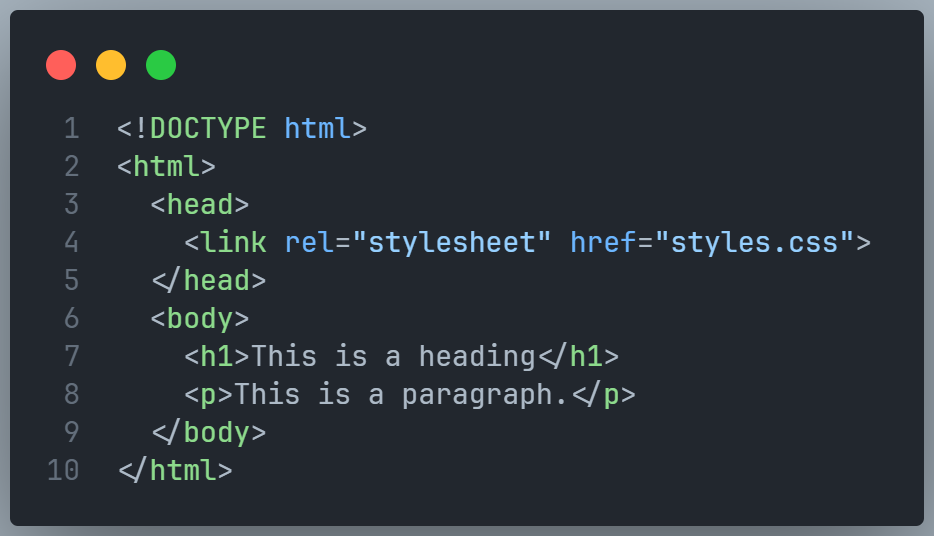
The external style sheet can be written in any text editor. The file must not contain any HTML code, and must be saved with a .css extension.
Here is what the "styles.css" file looks like:
